A Runoff-On-Grid Approach to Embed Hydrological Processes in Shallow Water Models
Catchment-scale hydrological models encountered dichotomies with the numerical hydrodynamic models when describing surface routing process. We propose a new modeling framework, the so-called “Runoff-On-Grid” approach, for embedding distributed process-based hydrological modeling into shallow water models, as an alternative to the traditional Fully Hydrodynamic Approach (also known as Rain-On-Grid). Antecedent Soil ...

HESS Opinions: Towards a common vision for the future of hydrological observatories
Abstract. The Unsolved Problems in Hydrology (UPH) initiative has emphasized the need to establish networks of multi-decadal hydrological observatories to tackle catchment-scale challenges on a global scale. The already existing monitoring infrastructures have provided an enormous amount of hydrometeorological data, which has helped gain detailed insights into the causality of ...

Exploring the use of random forest classifier with Sentinel-2 imagery in flooded area mapping
Floods are the most frequent type of natural disasters occurring worldwide. In 2021 alone, in fact, the majority of the recorded catastrophic events were floods, which also dominated in terms of the highest number of disaster-related fatalities according to the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED, Delforge ...

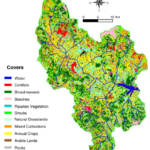
Assessing Multi-source Random Forest Classification and Robustness of Predictor Variables in Flooded Areas Mapping
Flood extent delineation techniques have benefited from the increasing availability of remote sensing imagery, classification techniques and the introduction of geomorphic descriptors derived from Digital Elevation Models (DEM). On the other hand, high-performing Machine Learning (ML) methods have allowed for the development of accurate flood maps by integrating several predictor ...

Advancing river monitoring using image-based techniques: Challenges and opportunities
Enhanced and effective hydrological monitoring plays a crucial role in understanding water-related processes in a rapidly changing world. Within this context, image-based river monitoring has shown to significantly enhance data collection, improve analysis and accuracy, and support effective and timely decision-making. The integration of remote and proximal sensing technologies, with ...

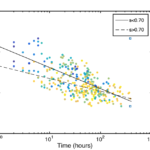
Are rainfall extremes intensifying in Southern Italy?
The growing number of extreme hydrological events observed worldwide has raised the level of attention towards the impact of climate change on the rainfall process, which is difficult to quantify given its strong spatial and temporal heterogeneity. Therefore, the impact of the climate change should be determined ranging from individual ...

Ensemble of optimised machine learning algorithms for predicting surface soil moisture content at a global scale
Accurate information on surface soil moisture (SSM) content at a global scale under different climatic conditions is important for hydrological and climatological applications. Machine-learning-based systematic integration of in situ hydrological measurements, complex environmental and climate data, and satellite observation facilitate the generation of reliable data products to monitor and analyse ...

Intercomparison of recent Microwave satellite Soil Moisture Products on European Ecoregions
The study centered on the comprehensive assessment of satellite-based microwave soil moisture (SM) products across Europe, taking into account crucial variables including geographical diversity, climate dynamics, and land cover variations. We systematically compared SM products from esteemed entities such as NASA, ESA, ASCAT, SENTINEL-1, and ESA's Climate Change Initiative against ...